fMRI data preprocessing¶
Segmentation¶
Segmentation splits an image into individual tissue types.
Why segment my data?
Segmentation refers to separating your data into different tissue types. Segmentation in SPM is done based on probability maps of six tissues: grey matter, white matter, cerebrospinal fluid, non-brain soft tissues, skull, and other (representing anything not captured by the previous maps). Knowing which voxels in your image belong to which tissue type can improve normalisation.
For a thorough overview of issues related to segmentation, see the SPM book:
-
From the SPM menu panel, select
Segment. You will see a pop-up window appear looking like this: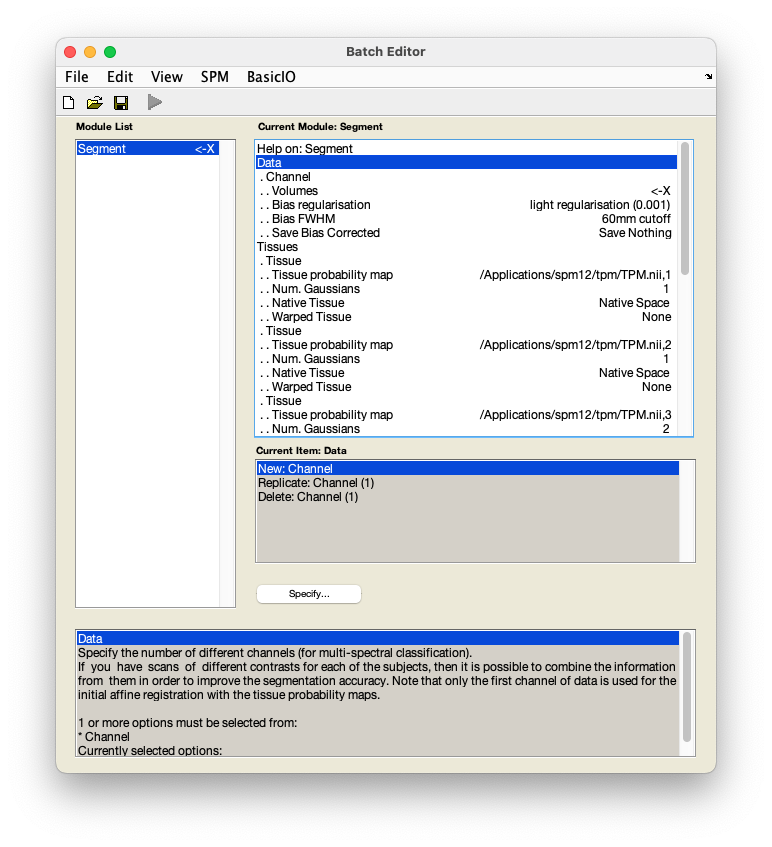
-
Select
DataVolumes. - In the pop-up window, use the left-hand panel to navigate to
sub-01/anat/. - From the right-hand panel, select the anatomical image
sub-01_T1w.niiand pressDone. - Select
Save bias correctedSave bias corrected. (This is calledSave INU correctedin more recent SPM versions.) - Select
Deformation fieldsForward. - Save this batch for future reference -
FileSave batchand name it, e.g.segmentation_batch.mat. - Run your batch by pressing .
SPM will now create tissue-specific images (prefixed c) and a bias-field corrected structural image (prefixed m). Additionally, a deformation field (prefixed y) will be generated, which contains three volumes to encode the x, y, and z coordinates. Given that the structural and functional data have been coregistered, this deformation field can be used in normalising the functional data.